Share WinXP Folders
Quick Overview: Tips for sharing folders on a Windows XP Home Network (XP Pro may differ - notably when 'simple file sharing' is disabled). We do not profess to be network gurus but have found that the information/guidance in the following paragraphs has usually ironed-out or at least identified any problems.
Which folders to share.
- Avoid sharing folders within the 'Documents and Settings' areas (this includes the My Documents folder) or the 'Windows' folder.
- Avoid sharing the whole (the root) of any drive letter.
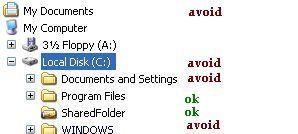
- It is generally a good policy to share newly created folders (just intended for sharing) or else some other folder such as a program's own folders often within the 'Program Files' folders area.
Sharing a chosen folder.
- Find the folder in MyComputer/Windows Explorer and Right Click on it.
- Choose properties from the list shown and go to the Sharing Tab.
- Leave local sharing and security alone and don't use the Wizard.
- If “Network sharing and security” shows the message: "If you
understand the security risks but want to share files without running
the wizard, click here". Click on the message. You may be given a second
prompt to confirm this action.
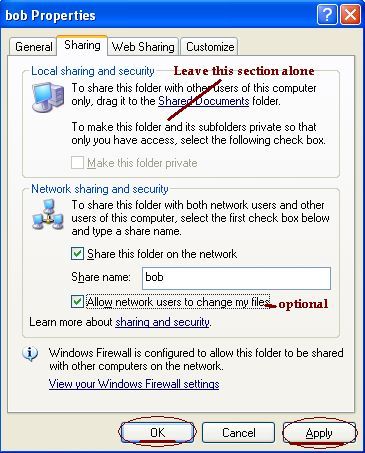
- Check the box “Share this folder on the network”
- Change the name to a simple one, not more than twelve characters, if necessary.
- Check the box “Allow network users to change my files” if you want to allow others to modify/create/delete files and sub-folders within the shared folder.
- Apply and OK your way out.
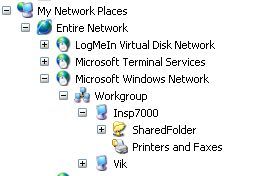
Accessing the shared folder.
- Simply open My Network Places if it shows-up from the Start Button.
- Right click My Computer and choose Explore. Then expand the boxes below My
Network Places till you find the PC and shared resource you want.
Some Troubleshooting
- Whether or not you are using a router 1 and sharing/access is being problematic then one of the first things to do is to disable or completely uninstall all software firewalls 2 running on all connected machines while you troubleshoot. If this makes you worried about security then disconnect the router from the internet while you troubleshoot. The native Windows firewall seldom blocks File Sharing but can also be disabled, if desired, from Control Panel >> Security Centre >> “Manage Security Settings” for Windows Firewall. We see it again and again and again where some (maybe obscure) firewall setting blocks the access you desire so we will say, once more, if access is affected ensure that no firewall can be responsible for it.
- It is best if all PCs sharing the same resources are in the same Workgroup. The current Workgroup name can be changed by right clicking on My Computer >> Properties >> Computer Name >> Change Button. You can then change both the PC's name and the current Workgroup name. A reboot is required. As with the names you have given to shared folders keep Workgroup and PC names simple and not more than 12 characters. Only alphanumeric with no spaces is recommended. Ensure that no two PCs on the network have the same name.
- When access problems occur it can be wise to turn off all PCs and the router and restart them all and then wait 5 minutes for the network to “sort itself out”. Networking "bed down" while all the hardware sorts itself out is far from immediate.
- You can always find out a PC's current network status by using the command
ipconfig /all
fom a command prompt (which itself can be opened by entering cmd into the run box from the Start menu). Note, in particular, the IP address value for the computer in question and the gateway value (which is usually the IP address of the router). One should get the following sort of output: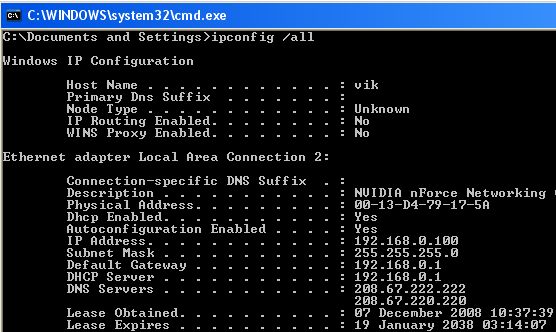
- Armed
with the IP addresses of the various machines you can then see if
pinging them from other PCs is successful or if they time out or give
other error messages. To ping by IP address you would again open a
command prompt and say issue the command:
ping 192.168.0.1
… which should result in the following sort of output when the pings are replied to:
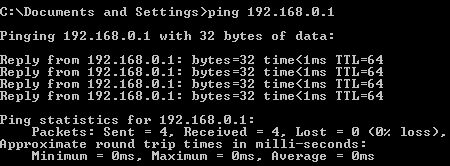
- If you don't get a response similar to the above then you have something affecting basic access to the PC in question. If you can't resolve this by running through the tips above you are likely to need to contact your Network Admin.
- One should also be able to ping by machine name (e.g. ping vik or ping insp7000) and if successful the associated IP address would be indicated in the responses. However pinging by IP address is the more basic and works at a lower level so is very important when troubleshooting network connections.
Network Interface Configuration
- The various installed network interfaces can be shown by going to "Internet Connections" from the
Control Panel. They can also be reached by a R-Click on Network Places (reached from the Start button
or within the My Computer tree) and then by choosing Properties. Select the relevant adapter that will be
connecting to your router (or occasionally to another specific PC if using DCC - Direct Cable Connection).
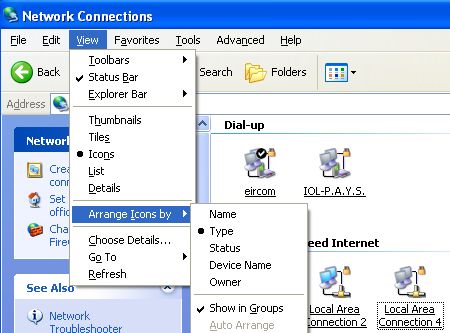
- You can adjust the layout to suit but we recommend that from the View Menu you choose "Icons" and elect to have them "Arranged by Type" and to "Show in Groups". Then R-Click on the relevant interface for the network involved and choose properties to see its particular configuration.
- As a minimum, the Client (Client for Microsoft Networks), the Service (File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft
Networks) and the Protocol (Internet Protocol) should all have been enabled and be in use. They are normally included
by default but would occasionally need to be installed and enabled if that is not the case.
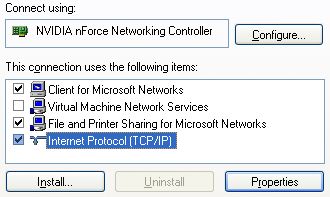
TCP/IP Settings
- TCP and IP are protocols involved in sending data across networks. Each network adapter needs to have its TCP/IP settings appropriately configured.
- Highlight the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) setting and choose its Properties.
- Unless there are special reasons to do otherwise, both settings (Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically) should be so enabled.
- IP addresses on the network are generally best allocated to each PC by ones router. A router is designed to be the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server for a network. A DHCP server allocates IP addresses and when IP addresses are automatically configured it is the router's DHCP server that normally does this seamlessly in the background.
- The DNS (Domain Name System) is just one way of linking the names of PCs to their IP addresses, which have been allocated by the DHCP server. DNS is mentioned here just for completeness. There are many other ways of associating the name and the IP address of a PC and they differ under different operating system. This particular area can “do ones head in” so we won't even start going into its complexities particularly since under WinXP running on a router it should be automatic.
Direct connection of two computers
- It should be relatively simple to set this up with two Windows XP machines. Just use a cross-over cable to connect PC to PC in place of the straight-through cable that is needed to connect each PC to a router, switch or hub. (On some modern hardware it doesn't matter which cable you use since the hardware can identify which sort of cable has been connected. At the moment this is not however commonplace). Converter jacks can also be obtained but in general try to minimise the number of connections used in such circuits.
- Although such cables have four "twisted-pairs" of wires only two pairs are in use for such networking.
With an RJ45 plug showing its metal connectors upmost then, from left to right, pins 1,2,3 and 6 are the only
ones of relevance. Commonly these are an orange/orange+white and a green/green+white pair.
Straight-through have the same arrangement at both ends; cross-over (as in Fig 1 below and which just for
clarity does not show the blue or brown pairs) have green and orange transposed as well as
green+white and orange+white transposed. One can simply just disregard the layout of pins 4, 5, 7 and 8 as far
as straightforward networking is concerned.
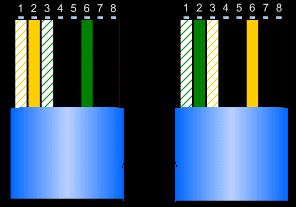
Fig 1. (From left to right; cross-over 568-B to 568-A). - Then follow the same general principles outlined above:-
1.Ensure you share a folder (or other resource) on each machine
2.Always use simple short names for PC/Workgroup/Shares
3.Have both PCs in the same workgroup
4.Each PC must have a unique name
5.Leave the TCP/IP settings on automatic; the two PCs when turned on should then negotiate the IP address allocation, etc, etc.
6.Reboot both PCs and leave a nice period before checking that sharing is as expected.
7.If there are problems then start pinging (including pinging ones own computer) and disabling firewalls, etc, etc. - Note. Just be aware that the term "patch cable" is sometimes used as a synonym for straight-through cable but it is also used to mean cable that has already had the connectors attached to it. We thus avoid the term.
Network Adapter/Card Uniqueness
- Every such adapter has a (virtually) unique identifying number. It is 6 pairs of hexadecimal digits and in the ipconfig /all results above was shown by Physical Address = 00-13-D4-79-17-5A and which is also known as its MAC address. This number is used on the network to identify a specific network adapter since a PC (typically one using both a wired and a wireless interface) can contain more than one of them.
Final troubleshooting tip
- We have no real rationale for the following but have resolved otherwise unresolvable Windows XP networking problems by "going back to square one" as far as possible.
- If using XP Pro and "Simple File Sharing" (My Computer - Tools - Folder Options - View) is not enabled then enable it.
- Unshare all shared folders on all relvant machines.
- Reboot machine after no shared folders.
- Set up shared folders from scratch.
- We have said it before but do ensure than no firewalls are blocking.
- Reboot machine. Reboot all.
Notes
- Routers are nowadays one of the most common things used to connect to a broadband ISP. Just as with firewalls they come in very many different flavours and can be configured in all sorts of ways. We will not attempt to go into all the specifics here but we did recently came across a page dealing with how some can be configured and thought, if nothing else, that it was a good read if you want to improve your understanding of this often tricky area. Most routers will come with a manual, probably on a CD, or which can be downloaded from the internet.
- Firewalls are designed to control access to and from computers. They are there to prevent unauthorised access but if malconfigured can actually prevent the normal and desired access of the internet or of other PCs on a network. Hardware firewalls often exist within routers where they normally protect the local area network from most undesirable outside access. Windows XP and above have a native software firewall that can prevent undesired ingress from outside but which does little to stop the egress of illicit information out from a PC. Software personal firewalls come in very many shapes and forms and configurations. Malconfigured software firewalls are one of the most common reasons for networks not working as they should. At the expense of repetition we say yet again: "disable and even uninstall all firewalls when troubleshooting network access problems".
- Microfilters are small matchbox-sized gizmos that should be placed on ALL telephone jacks when upgrading (especially from dial-up) to ADSL broadband. Attaching any telephone lines (including those coming from a dial-up modem) to such a jack lacking a microfilter will usually destroy your broadband internet connection. We see this as a recurring problem notably in those areas which have just been upgraded to ADSL broadband; the broadband that shares access down telephone lines.